Enhance Job Performance with RainierGPR Concrete Scanning Services
Enhance Job Performance with RainierGPR Concrete Scanning Services
Blog Article
Discovering the Midst: A Comprehensive Overview to Concrete Scanning and Its Diverse Applications
In the realm of building and framework growth, the precise procedure of concrete scanning holds a crucial role in guaranteeing the architectural stability and security of jobs. As modern technology remains to evolve, the applications of concrete scanning have actually expanded far past simple surface-level analyses. From identifying rebar and post-tension cords to drawing up voids and conduits concealed within concrete structures, the abilities of modern-day scanning methods are both excellent and important. However, the real depth of concrete scanning's prospective reaches also better, branching right into unforeseen sectors and triggering ingenious remedies. The interconnected web of possibilities that concrete scanning offers is not only fascinating but also essential for the advancement of different industries.
Importance of Concrete Scanning
Comprehending the significance of concrete scanning is critical in making sure the security and honesty of frameworks during building and construction and remodelling projects. Concrete scanning utilizes innovative innovations such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electro-magnetic induction to find ingrained things, spaces, or various other abnormalities within concrete structures.
Furthermore, concrete scanning plays a pivotal duty in guaranteeing conformity with building ordinance and laws that mandate the security of existing architectural components during construction tasks. By accurately drawing up the internal make-up of concrete, scanning modern technologies allow construction experts to make enlightened choices that support the architectural security and durability of buildings and framework projects. Essentially, the importance of concrete scanning hinges on its ability to guard both the structural honesty and the personnel included in construction undertakings.
Technologies Used in Concrete Scanning
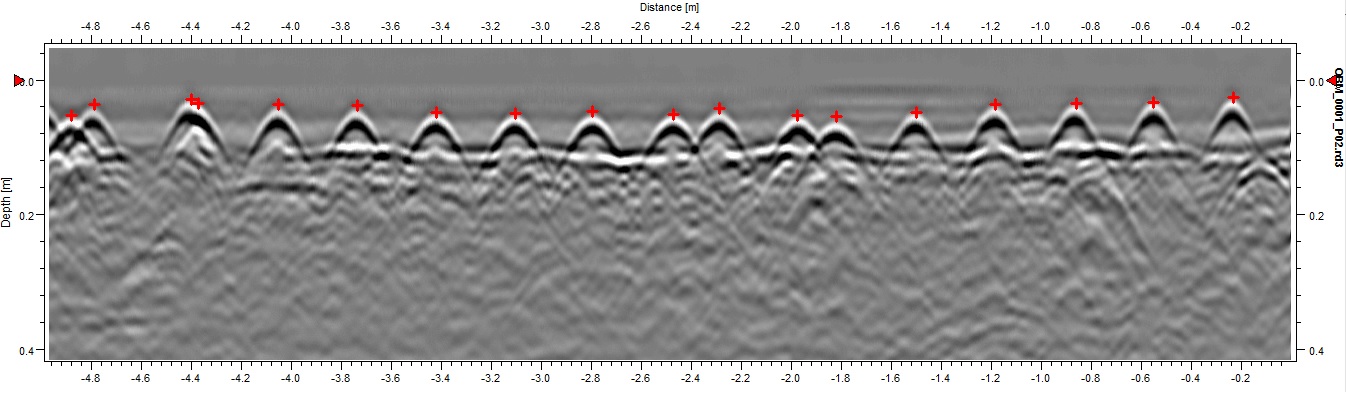
Concrete scanning depends on innovative technologies such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electro-magnetic induction to properly spot embedded things and anomalies within concrete structures. Ground-penetrating radar runs by producing high-frequency electromagnetic waves right into the concrete. When these waves experience various products or spaces within the concrete, they get better to the surface area, enabling the GPR system to develop a thorough subsurface photo. This innovation is specifically reliable in situating rebar, post-tension cables, conduits, and other things installed in concrete.
Electro-magnetic induction, on the various other hand, functions by producing magnetic fields around a concrete framework with a transmitter coil. When metal objects exist within the concrete, they interfere with these electro-magnetic fields, causing eddy currents to flow with the metal. By measuring the adjustments in the electro-magnetic areas with a receiver coil, the system can determine the place of metallic things in the concrete.
These sophisticated technologies play a vital function in non-destructive testing, making certain the security and integrity of concrete frameworks in different industries.
Applications in Building And Construction Industry
Within the building and construction sector, concrete scanning innovation finds diverse applications that enhance task efficiency and security. One key application is the discovery of rebar, post-tension cords, and other embedded items before drilling or reducing into concrete structures. By accurately drawing up these elements, construction groups can stay clear of expensive problems, make sure architectural stability, and stop potential security hazards. Furthermore, concrete scanning is utilized for situating spaces, such as my latest blog post air pockets or locations of wear and tear within concrete, which can endanger the total stamina of a framework. By identifying these spaces early, building specialists can take necessary procedures to address them and preserve the toughness of the building. Additionally, concrete scanning plays an essential role in quality assurance by verifying the thickness of concrete covers over support, making certain compliance with layout specifications and standards. On the whole, the applications of concrete scanning in the construction sector contribute substantially to streamlining job operations, reducing dangers, and supplying top quality results.
Safety Benefits of Concrete Scanning
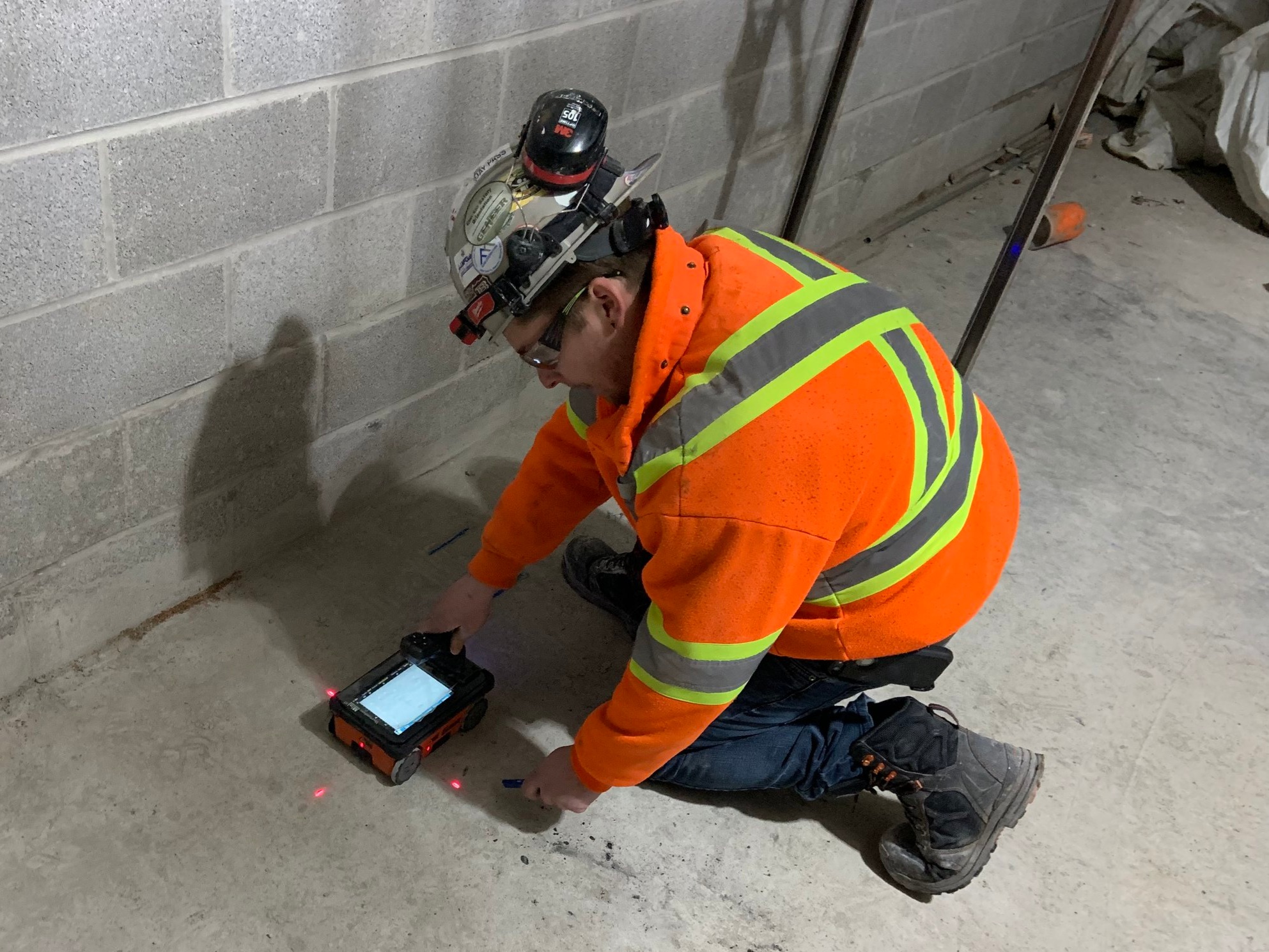
In the world of building safety and security, the application of concrete scanning modern technology provides an extremely important advantage in preemptively recognizing prospective dangers and fortifying structural stability. By making use of advanced scanning approaches such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electro-magnetic induction, building and construction groups can accurately find rebar, post-tension cable televisions, avenues, and various other hidden objects within concrete frameworks. This positive technique significantly decreases the danger of unintended strikes during boring, reducing, or coring tasks, therefore avoiding pricey problems, injuries, and task hold-ups.
In addition, concrete scanning enhances employee security by offering real-time details regarding the architectural condition of concrete components. By resolving prospective safety concerns promptly, concrete scanning adds to creating a safe and secure working setting and mitigating the probability of structural failures or accidents on building and construction sites.
Future Fads in Concrete Scanning
Arising innovations in scanning technology are poised to change the field of concrete assessment and evaluation. By using the power of AI, Click This Link these systems can analyze huge amounts of data collected during scanning processes to give more accurate and comprehensive understandings into the condition of concrete structures.
Another significant trend is the development of more portable and easy to use scanning gadgets. Miniaturization of scanning tools permits for less complicated access to confined spaces and remote places, making assessments a lot more effective and detailed. Additionally, advancements in wireless interaction technologies enable real-time information transfer and evaluation, facilitating quicker decision-making processes.
Moreover, there is an expanding concentrate on sustainability in concrete scanning technologies - RainierGPR Concrete Scanning. Manufacturers are significantly incorporating environmentally friendly materials and energy-efficient features into their tools to lower environmental impact. These future fads are established to improve the efficiency, precision, and sustainability of concrete scanning techniques, shaping the industry's future landscape
Final Thought
In verdict, concrete scanning plays an essential function in the building and construction industry by ensuring the safety and security and efficiency of various tasks. As innovation advancements, the future of concrete scanning holds encouraging developments for you could try these out enhancing construction processes.

Report this page